flume的工作流程及操作
1 什么是flume
Flume是一个分布式的、可靠的、高可用的数据采集、聚合和大型数据很迁移(log)系统。
web server.log
| ipaddr | visittime | visiturl | duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| ip地址 | 访问时间 | 来访url | 停留时长 |
这些日志有啥用?
- 观看了哪些视频
- 视频看没看完
- 通过哪些外部链接访问本网站(广告投放)
- 每天在哪个时间段访问的频次较高
2. 什么时候用Flume?
需要进行数据采集时。
3 Flume体系
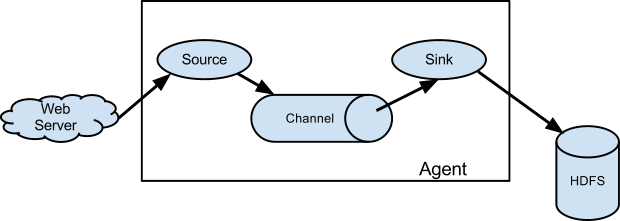
- Event:消息,事件,在Flume中数据传输的单位是“event”,Flume将解析的日志数据、接收到的TCP数据等分装成events在内部Flow中传递。
- Agent:临近数据源(比如logs文件)的、部署在宿主机器上的Flume进程,通常用于收集、过滤、分拣数据,Flume Agent通常需要对源数据进行“修饰”后转发给远端的Collector。
- 外部source以flume能识别的数据向flume发送事件
- 可以是Avro clients、other Flume agents、Thrift clients written
- source接受一个事件,就将存储在一个或多个channels
- source:用于配置数据采集的方式(http, localFileSystem, Tcp)
- channel保存事件并且存储, 直到sink 拉取数据
- memory channel:临时内存存储
- filechannel: checkpoint、datadir 先把数据存储到本地,再进行数据传输
- sink 从channel移除事件并且将event放到外部仓库上,比如hdfs, 或者转发给下一个Flume agent中的 source
- sink:配置数据存储的目的地(HDFS、 本地文件系统、logger、http)
组件内部的关系
- 一个Source可以将events传送给一个或者多个Channel,通常一个Source对应一个Channel
- 一个Channel可以接入多个Sources,即多个Sources可以将events发给一个Channel。同时多个Sinks可以从一个Channel中消费消息
- Sink的上游为Channel,一个Sink只能从一个Channel中消费消息。
- Source将消息传送给Channel,以及Sink从Channel中消费消息,均为在内部的事务中进行。
source 和 sink 是异步执行的
#### 3.1 可靠性
events 存储在每个agent的channel中。然后events事件流到下一个agent或终端如hdfs中。只有当这些events存储在hdfs或下一个agent的channel中才会将原来的events删除。
flume 通过事务保证event交付的可靠性。
3.2 可恢复性
Flume支持一个由本地文件系统支持的持久化文件通道。
将event保存在内存中,如果发生故障数据是无法恢复的。当然在内存中速度会更快。
3.3 Flume常用组件
- source
- exec source
- spooling directory source
- channel
- memory channel
- file channel
- sink
- logger sink
- hdfs sink
4 Flume 常用操作
4.1 常用配置
# 每个组件的名称
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# netcat监控方式、监控的ip:localhost、端口:44444
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# sink 的方式 logger
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# 写入到内存、
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
# 绑定source和sink到channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
4.2 Source
Exec source
通过Linux命令(cat [name pipe] or tail -F [file])监控指定文件的日志, 如果源意外退出,将不会产生更多数据。
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
# 指定类型、命令
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /var/log/secure
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
Spooling Directory Source
允许将数据放在磁盘上,比exec source更具可靠性,数据不会丢失,但效率更比exec source低。
a1.channels = ch-1
a1.sources = src-1
fs.sources.r3.type=spooldir
fs.sources.r3.spoolDir=/opt/modules/apache-flume-1.6.0-bin/flume_template
fs.sources.r3.fileHeader=true
fs.sources.r3.ignorePattern=^(.)*\\.out$ # 过滤out结尾的文件
Spooling Directory Source 详细参数
4.3 Channel
Memory Channel
数据在内存中,临时存储
a1.channels = c1
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.byteCapacityBufferPercentage = 20
a1.channels.c1.byteCapacity = 800000
File Channel
先把数据存储到本地,再进行数据传输,增加可靠性
a1.channels = c1
a1.channels.c1.type = file
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir = /mnt/flume/checkpoint
a1.channels.c1.dataDirs = /mnt/flume/data
Sink
Info级别日志等级,通常用于测试环境/调试
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
HDFS Sink
事件下沉到HDFS上。它支持序列文件和txt文本文件。
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/events/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events-
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
5 实战
5.1 hive source(实时采集hive日志)
hive.sources = r2
hive.channels = c2
hive.sinks = k2
# define sources
hive.sources.r2.type = exec
hive.sources.r2.command = tail -F /var/log/secure
hive.sources.r2.shell = /bin/bash -c
hive.sources.r2.logStdErr = false
hive.sources.r2.channels = c2
# def channels
hive.channels.c2.type = memory
hive.channels.c2.capacity = 10000
hive.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
# def sinks
hive.sinks.k2.type = hdfs
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop1:8020/user/root/flume-hive/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.writeFormat = Text
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 10
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 30
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 0
hive.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0
hive.sources.r2.channels = c2


